How to Structure a Dissertation – A Step by Step Guide
Published by at August 11th, 2021 , Revised On September 20, 2023
A dissertation – sometimes called a thesis – is a long piece of information backed up by extensive research. This one, huge piece of research is what matters the most when students – undergraduates and postgraduates – are in their final year of study.
On the other hand, some institutions, especially in the case of undergraduate students, may or may not require students to write a dissertation. Courses are offered instead. This generally depends on the requirements of that particular institution.
If you are unsure about how to structure your dissertation or thesis, this article will offer you some guidelines to work out what the most important segments of a dissertation paper are and how you should organise them. Why is structure so important in research, anyway?
One way to answer that, as Abbie Hoffman aptly put it, is because: “Structure is more important than content in the transmission of information.”
Also Read: How to write a dissertation – step by step guide.
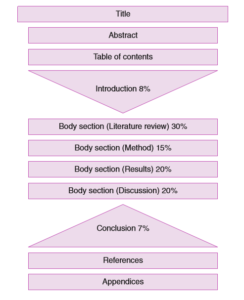
How to Structure a Dissertation or Thesis
It should be noted that the exact structure of your dissertation will depend on several factors, such as:
- Your research approach (qualitative/quantitative)
- The nature of your research design (exploratory/descriptive etc.)
- The requirements set for forth by your academic institution.
- The discipline or field your study belongs to. For instance, if you are a humanities student, you will need to develop your dissertation on the same pattern as any long essay.
This will include developing an overall argument to support the thesis statement and organizing chapters around theories or questions. The dissertation will be structured such that it starts with an introduction, develops on the main idea in its main body paragraphs and is then summarised in conclusion.
However, if you are basing your dissertation on primary or empirical research, you will be required to include each of the below components. In most cases of dissertation writing, each of these elements will have to be written as a separate chapter.
But depending on the word count you are provided with and academic subject, you may choose to combine some of these elements.
For example, sciences and engineering students often present results and discussions together in one chapter rather than two different chapters.
If you have any doubts about structuring your dissertation or thesis, it would be a good idea to consult with your academic supervisor and check your department’s requirements.
Parts of a Dissertation or Thesis
Title Page
Your dissertation will start with a title page that will contain details of the author/researcher, research topic, degree program (the paper is to be submitted for), and research supervisor. In other words, a title page is the opening page containing all the names and title related to your research.
The name of your university, logo, student ID and submission date can also be presented on the title page. Many academic programs have stringent rules for formatting the dissertation title page.
Acknowledgements
The acknowledgments section allows you to thank those who helped you with your dissertation project. You might want to mention the names of your academic supervisor, family members, friends, God, and participants of your study whose contribution and support enabled you to complete your work.
However, the acknowledgments section is usually optional.
Tip: Many students wrongly assume that they need to thank everyone…even those who had little to no contributions towards the dissertation. This is not the case. You only need to thank those who were directly involved in the research process, such as your participants/volunteers, supervisor(s) etc.
Abstract
Perhaps the smallest yet important part of a thesis, an abstract contains 5 parts:
- A brief introduction of your research topic.
- The significance of your research.
- A line or two about the methodology that was used.
- The results and what they mean (briefly); their interpretation(s).
- And lastly, a conclusive comment regarding the results’ interpretation(s) as conclusion.
Stuck on a difficult dissertation? We can help!
Our Essay Writing Service Features:
- Expert UK Writers
- Plagiarism-free
- Timely Delivery
- Thorough Research
- Rigorous Quality Control
“Our expert dissertation writers can help you with all stages of the dissertation writing process including topic research and selection, dissertation plan, dissertation proposal, methodology, statistical analysis, primary and secondary research, findings and analysis and complete dissertation writing. “
Tip: Make sure to highlight key points to help readers figure out the scope and findings of your research study without having to read the entire dissertation. The abstract is your first chance to impress your readers. So, make sure to get it right. Here are detailed guidelines on how to write abstract for dissertation.
Table of Contents
Table of contents is the section of a dissertation that guides each section of the dissertation paper’s contents. Depending on the level of detail in a table of contents, the most useful headings are listed to provide the reader the page number on which said information may be found at.
Table of contents can be inserted automatically as well as manually using the Microsoft Word Table of Contents feature.
List of Figures and Tables
If your dissertation paper uses several illustrations, tables and figures, you might want to present them in a numbered list in a separate section. Again, this list of tables and figures can be auto-created and auto inserted using the Microsoft Word built-in feature.
List of Abbreviations
Dissertations that include several abbreviations can also have an independent and separate alphabetised list of abbreviations so readers can easily figure out their meanings.
Glossary
If you think you have used terms and phrases in your dissertation that readers might not be familiar with, you can create a glossary that lists important phrases and terms with their meanings explained.
Looking for dissertation help?
ResearchProspect to the rescue then!
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with quantitative dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!
Introduction
Introduction chapter briefly introduces the purpose and relevance of your research topic.
Here, you will be expected to list the aim and key objectives of your research so your readers can easily understand what the following chapters of the dissertation will cover. A good dissertation introduction section incorporates the following information:
- It provides background information to give context to your research.
- It clearly specifies the research problem you wish to address with your research. When creating research questions, it is important to make sure your research’s focus and scope are neither too broad nor too narrow.
- it demonstrates how your research is relevant and how it would contribute to the existing knowledge.
- It provides an overview of the structure of your dissertation. The last section of an introduction contains an outline of the following chapters. It could start off with something like: “In the following chapter, past literature has been reviewed and critiqued. The proceeding section lays down major research findings…”
- Theoretical framework – under a separate sub-heading – is also provided within the introductory chapter. Theoretical framework deals with the basic, underlying theory or theories that the research revolves around.
All the information presented under this section should be relevant, clear, and engaging. The readers should be able to figure out the what, why, when, and how of your study once they have read the introduction. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to structure the introduction to the dissertation.
“Overwhelmed by tight deadlines and tons of assignments to write? There is no need to panic! Our expert academics can help you with every aspect of your dissertation – from topic creation and research problem identification to choosing the methodological approach and data analysis.”
Literature Review
The literature review chapter presents previous research performed on the topic and improves your understanding of the existing literature on your chosen topic. This is usually organised to complement your primary research work completed at a later stage.
Make sure that your chosen academic sources are authentic and up-to-date. The literature review chapter must be comprehensive and address the aims and objectives as defined in the introduction chapter. Here is what your literature research chapter should aim to achieve:
- Data collection from authentic and relevant academic sources such as books, journal articles and research papers.
- Analytical assessment of the information collected from those sources; this would involve a critiquing the reviewed researches that is, what their strengths/weaknesses are, why the research method they employed is better than others, importance of their findings, etc.
- Identifying key research gaps, conflicts, patterns, and theories to get your point across to the reader effectively.
While your literature review should summarise previous literature, it is equally important to make sure that you develop a comprehensible argument or structure to justify your research topic. It would help if you considered keeping the following questions in mind when writing the literature review:
- How does your research work fill a certain gap in exiting literature?
- Did you adopt/adapt a new research approach to investigate the topic?
- Does your research solve an unresolved problem?
- Is your research dealing with some groundbreaking topic or theory that others might have overlooked?
- Is your research taking forward an existing theoretical discussion?
- Does your research strengthen and build on current knowledge within your area of study? This is otherwise known as ‘adding to the existing body of knowledge’ in academic circles.
Tip: You might want to establish relationships between variables/concepts to provide descriptive answers to some or all of your research questions. For instance, in case of quantitative research, you might hypothesise that variable A is positively co-related to variable B that is, one increases and so does the other one.
Research Methodology
The methods and techniques (secondary and/or primary) employed to collect research data are discussed in detail in the Methodology chapter. The most commonly used primary data collection methods are:
- questionnaires
- interviews
- surveys
- focus groups
- observations
Essentially, the methodology chapter allows the researcher to explain how he/she achieved the findings, why they are reliable and how they helped him/her test the research hypotheses or address the research problem.
You might want to consider the following when writing methodology for the dissertation:
- Type of research and approach your work is based on. Some of the most widely used types of research include experimental, quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
- Data collection techniques that were employed such as questionnaires, surveys, focus groups, observations etc.
- Details of how, when, where, and what of the research that was conducted.
- Data analysis strategies employed (for instance, regression analysis).
- Software and tools used for data analysis (Excel, STATA, SPSS, lab equipment, etc.).
- Research limitations to highlight any hurdles you had to overcome when carrying our research. Limitations might or might not be mentioned within research methodology. Some institutions’ guidelines dictate they be mentioned under a separate section alongside recommendations.
- Justification of your selection of research approach and research methodology.
Here is a comprehensive article on how to structure a dissertation methodology.
Research Findings
In this section, you present your research findings. The dissertation findings chapter is built around the research questions, as outlined in the introduction chapter. Report findings that are directly relevant to your research questions.
Any information that is not directly relevant to research questions or hypotheses but could be useful for the readers can be placed under the Appendices.
As indicated above, you can either develop a standalone chapter to present your findings or combine them with the discussion chapter. This choice depends on the type of research involved and the academic subject, as well as what your institution’s academic guidelines dictate.
For example, it is common to have both findings and discussion grouped under the same section, particularly if the dissertation is based on qualitative research data.
On the other hand, dissertations that use quantitative or experimental data should present findings and analysis/discussion in two separate chapters. Here are some sample dissertations to help you figure out the best structure for your own project.
Tip: Try to present as many charts, graphs, illustrations and tables in the findings chapter to improve your data presentation. Provide their qualitative interpretations alongside, too. Refrain from explaining the information that is already evident from figures and tables.
Discussion
The findings are followed by the Discussion chapter, which is considered the heart of any dissertation paper. The discussion section is an opportunity for you to tie the knots together to address the research questions and present arguments, models and key themes.
This chapter can make or break your research.
The discussion chapter does not require any new data or information because it is more about the interpretation(s) of the data you have already collected and presented. Here are some questions for you to think over when writing the discussion chapter:
- Did your work answer all the research questions or tested the hypothesis?
- Did you come up with some unexpected results for which you have to provide an additional explanation or justification?
- Are there any limitations that could have influenced your research findings?
Here is an article on how to structure a dissertation discussion.
Conclusion
Conclusions corresponding to each research objective are provided in the Conclusion section. This is usually done by revisiting the research questions to finally close the dissertation. Some institutions may specifically ask for recommendations to evaluate your critical thinking.
By the end, the readers should have a clear apprehension of your fundamental case with a focus on what methods of research were employed and what you achieved from this research.
Quick Question:
Does the conclusion chapter reflect on the contributions your research work will make to existing knowledge?
Answer: Yes, the conclusion chapter of the research paper typically includes a reflection on the research’s contributions to existing knowledge. In the “conclusion chapter”, you have to summarise the key findings and discuss how they add value to the existing literature on the current topic.
Reference list
All academic sources that you collected information from should be cited in-text and also presented in a reference list (or a bibliography in case you include references that you read for the research but didn’t end up citing in the text), so the readers can easily locate the source of information when/if needed.
At most UK universities, Harvard referencing is the recommended style of referencing. It has strict and specific requirements on how to format a reference resource. Other common styles of referencing include MLA, APA, Footnotes, etc.
Appendices
Each chapter of the dissertation should have relevant information. Any information that is not directly relevant to your research topic but your readers might be interested in (interview transcripts etc.) should be moved under the Appendices section.
Things like questionnaires, survey items or readings that were used in the study’s experiment are mostly included under appendices.
An Outline of Dissertation/Thesis Structure
How can We Help you with your Dissertation?
If you are still unsure about how to structure a dissertation or thesis, or simply lack the motivation to kick start your dissertation project, you might be interested in our dissertation services.
If you are still unsure about how to structure a dissertation or thesis, or lack the motivation to kick start your dissertation project, you might be interested in our dissertation services.
Whether you need help with individual chapters, proposals or the full dissertation paper, we have PhD-qualified writers who will write your paper to the highest academic standard. ResearchProspect is UK-based, and a UK-registered business, which means the UK consumer law protects all our clients.
All You Need to Know About Us Learn More About Our Dissertation Services
FAQs About Structure a Dissertation
The title page will contain details of the author/researcher, research topic, degree program (the paper is to be submitted for) and research supervisor’s name(s). The name of your university, logo, student number and submission date can also be presented on the title page.
The acknowledgements section allows you to thank those who helped you with your dissertation project. You might want to mention the names of your academic supervisor, family members, friends, God and participants of your study whose contribution and support enabled you to complete your work.
Yes, but only if you think that your paper does not contain any terms or phrases that the reader might not understand. If you think you have used them in the paper, you must create a glossary that lists important phrases and terms with their meanings explained.
Any information that is not directly relevant to research questions or hypotheses but could be useful for the readers can be placed under the Appendices, such as questionnaire that was used in the study.
You can use any of the referencing styles such as APA, MLA, and Harvard, according to the recommendation of your university; however, almost all UK institutions prefer Harvard referencing style.
References contain all the works that you read up and used and therefore, cited within the text of your thesis. However, in case you read on some works and resources that you didn’t end up citing in-text, they will be referenced in what is called a bibliography.
Additional readings might also be present alongside each bibliography entry for readers.