A research design is the roadmap that guides your entire research process. It connects your research question to the appropriate data collection and analysis techniques, ensuring that your findings are accurate, meaningful, and relevant.
A carefully planned research design:
- Defines the methodology
- Establishes the sample and variables
- Determines data collection and analysis techniques
- Maintains reliability and validity
- Addressed ethical concerns
- Ensures the study can be replicated
DO YOU KNOW?
A weak research design = weak and unreliable results
A strong research design = credible research with impactful findings
Why is a research design important?
A research design:
- Prevents bias during data collection and analysis
- Helps manage time, resources, and feasibility
- Ensures ethical and legal compliance
- Provides structured decision-making
- Justifies methodological choices to supervisors and reviewers
It also influences how your dissertation or research paper is graded. A solid structure builds confidence in the conclusions drawn.
Looking for dissertation help?
Research Prospect to the rescue then!
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety of disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!
Research Design Example
This study adopts a mixed-methods descriptive research design to evaluate the impact of digital learning tools on student performance. Quantitative data will be collected using structured questionnaires distributed to 200 university students. Qualitative insights will be gathered through six semi-structured interviews with educators. Quantitative data will be analysed using SPSS for descriptive statistics and regression testing, while qualitative responses will undergo thematic analysis. Ethical approval will be obtained, ensuring informed consent and confidentiality.
Types of Research Design
The research design has five types: descriptive, experimental, correlational, diagnostic, and explanatory.
| Research Design Type | Purpose | Example Study |
|---|---|---|
| Descriptive | Describes characteristics of a population or situation | Prevalence of diabetes among adults in London. |
| Experimental | Test cause-and-effect relationships | Effect of a new drug on the recovery rate. |
| Correlational | Measures the statistical relationship between variables | Link between exercise frequency and mental health. |
| Diagnostic | Identify causes and solutions for a problem | Reason behind software failure in an organisation. |
| Explanatory | Explain why a relationship exists | Why do students with sleep issues perform poorly? |
What are the types of a research design?
Types of research design are:
- Descriptive
- Experimental
- Correlational
- Diagnostic
- Explanatory
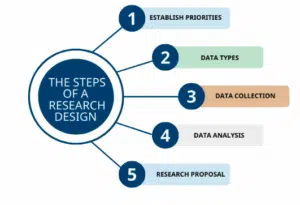
Step 1: Establish your research priorities
The first step is to establish your research priorities and objectives. The research design depends on the researcher’s priorities.
For a complex research study involving multiple methods, you may choose to have more than one research design. Multimethodology, or multimethod research, involves using more than one data collection or research method in a study or set of related studies.
If one research design is weak in one area, then another research design can cover that weakness. For instance, a dissertation analysing different situations or cases will have more than one research design.
For example
- Experimental research involves experimental investigation and laboratory experience, but it does not accurately investigate the real world.
- Quantitative research is good for the statistical part of the project, but it may not provide an in-depth understanding of the topic.
- Also, correlational research will not provide experimental results because it is a technique that assesses the statistical relationship between two variables.
While scientific considerations are a fundamental aspect of the research design, it is equally important that the researcher thinks practically before deciding on its structure. Here are some questions that you should think of:
Q1: Do you have enough time to gather data and complete the write-up?
Q2: Will you be able to collect the necessary data by interviewing a specific person or visiting a specific location?
Q3: Do you have in-depth knowledge about the different statistical analysis and data collection techniques to address the research questions or test the hypothesis?
Step 2: Identify the type of data required
Decide on the type of data you need for your research. The type of data you need to collect depends on your research questions or hypothesis. Two types of research data can be used to answer the research questions:
Primary Data vs. Secondary Data
| Primary Data | The researcher collects the primary data from first-hand sources with the help of different data collection methods, such as interviews, experiments, surveys, etc. Primary research data is considered far more authentic and relevant, but it involves additional cost and time. |
| Secondary Data | Research on academic references, which themselves incorporate primary data, will be regarded as secondary research data. There is no need to do a survey or interview with a person directly, and it is time-effective. The researcher should focus on the validity and reliability of the source. |
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data
| Qualitative Data | This type of data encircles the researcher’s descriptive experience and shows the relationship between the observation and the collected data. It involves interpretation and conceptual understanding of the research. There are many theories involved that can approve or disapprove the mathematical and statistical calculation. For instance, you are searching for how to write a research design proposal. It means you require qualitative data about the mentioned topic. |
| Quantitative Data | If your research requires statistical and mathematical approaches for measuring the variable and testing your hypothesis, your objective is to compile quantitative data. Many businesses and researchers use this type of data with pre-determined data collection methods and variables for their research design. |
Step 3: Select data collection methods
Once you have selected the type of research to answer your research question, you need to decide where and how to collect the data. It is time to determine your research method to address the research problem.
Research methods involve procedures, techniques, materials, and tools used for the study. For instance, a dissertation research design includes different resources and data collection techniques and helps establish your dissertation’s structure.
The following table shows the characteristics of the most popularly employed research methods:
| Data Collection Methods | What to consider |
|---|---|
| Surveys | The survey planning requires: Selection of responses and how many responses are required for the research? Survey distribution techniques (online, by post, in person, etc.) Techniques for designing the question |
| Interviews | Criteria to select the interviewee. Time and location of the interview. Type of interviews: i.e., structured, semi-structured, or unstructured |
| Experiments | Place of the experiment: laboratory or in the field. Measuring the variables Design of the experiment |
| Secondary Data | Criteria to select the references and sources for the data. The reliability of the references. The technique used for compiling the data source. |
Step 4: Data analysis procedures
Using the appropriate data and statistical analysis technique is necessary for the validity of your research. Choosing an appropriate analysis method is the final step for the research design. It can be split into two main categories:
-
Quantitative data analysis
The quantitative data analysis technique involves analysing the numerical data with the help of different applications such as SPSS, STATA, Excel, and OriginLab. This data analysis strategy tests different variables such as spectrum, frequencies, averages, and more.
-
Qualitative data analysis
Qualitative data analysis involves analysing figures, themes, and words, allowing for flexibility and the inclusion of the researcher’s subjective opinions. This means that the researcher’s primary focus will be interpreting patterns, tendencies, and accounts, and understanding the implications and social framework.
Step 5: Write your research proposal
When your research design is complete, you can add it to your research proposal, as it outlines the project’s execution. You can share it with the supervisor, who would evaluate the feasibility and capacity of the results and conclusions.
The research proposal is written in the future tense because you are writing your proposal before conducting research. The research methodology or research design, on the other hand, is generally written in the past tense.
What are the steps to write a research design?
- Establish your research priorities
- Identify the type of data required
- Select data collection methods
- Data analysis procedures
- Write your research proposal
Struggling to Write Your Research Design?
If you don’t know how to write your research design, don’t get worried. Get help from professional dissertation writing services. They have writers with years of experience creating research designs that align with the dissertation’s aim and objectives. They can also help you with the full dissertation paper.
Frequently Asked Questions
Research design is a systematic plan that guides the research process, outlining the methodology and procedures for collecting and analysing data. It ensures the research question is answered effectively, reliably, and validly.
Clarity, feasibility, ethical compliance, valid methodology, and logical alignment with research objectives make a good research design.
Research design is the overall research plan, while methodology includes the specific tools and techniques used to execute that plan.
Yes, especially in mixed-method studies, where both qualitative and quantitative designs are used.
A research design section should typically be around 800-2000 words, depending on academic level and university guidelines.