Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness.
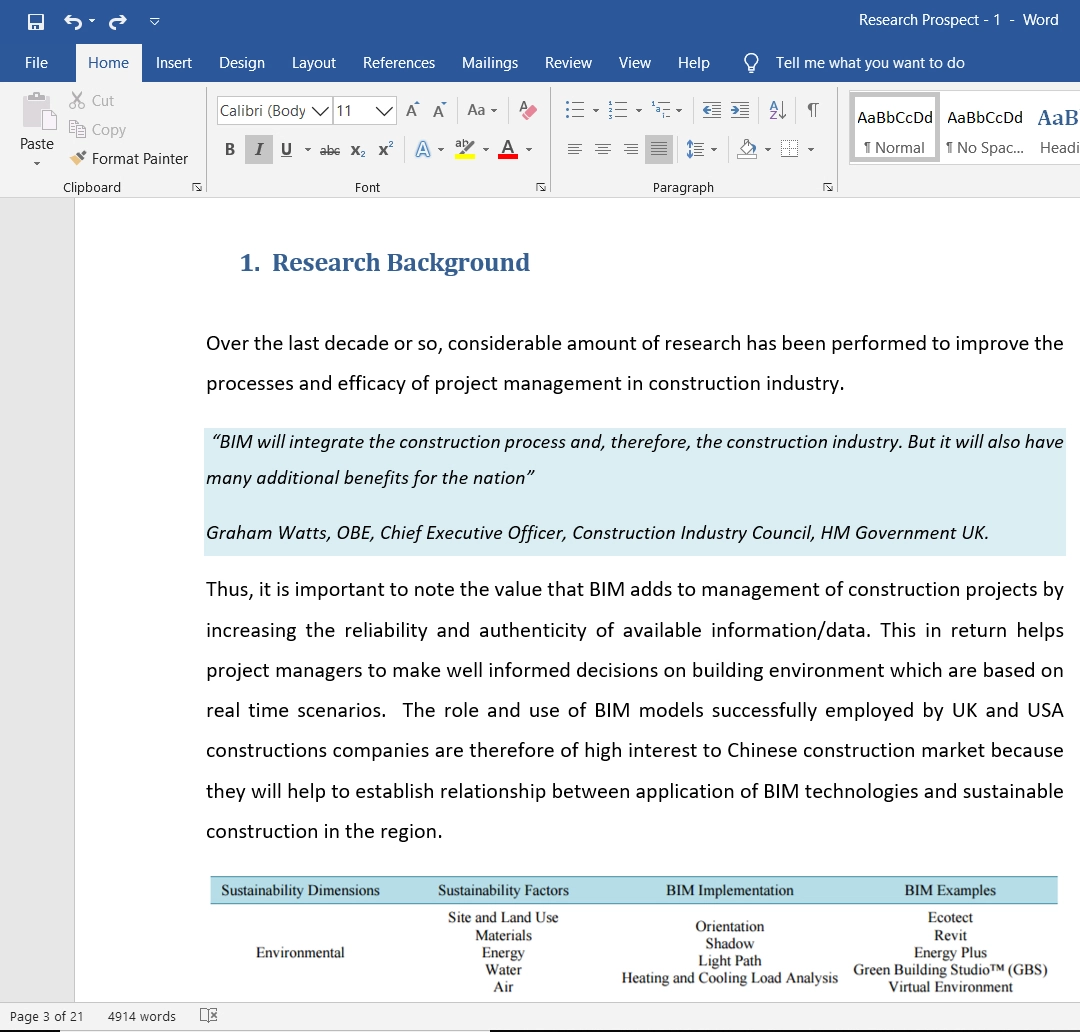
Interserve plc is a multinational company providing equipment, support, and construction businesses globally. Interserve provides advice on design, construction, and equipment to be used by its consumers globally. Organisations or companies with clear and easily understood policies, missions, and purposes unite their employees and ensure to navigate the organisation toward achieving its objectives.
The main goal or purpose of an organisation is why the organisation exists and the problem the organisation developed to provide. The purpose of an organisation should be brief and easily understood to ensure the employees remember it during their daily activities, thereby providing meaning through their work.
This motivates, inspires, and energises the employees and the organisation to move forward when they identify the reason or goal for doing the business. Purpose ensures the organisation is utilising its resources fully, for when they know and focus on what they do best; it will free resources that are not useful to them and utilise those that are useful entirely.
Furthermore, purpose ensures an organisation maintains a competitive advantage by looking for the difference in their customers’ needs and wants. This ensures that the organisation continually evolves to keep up with the change in consumer tastes and stay competitive. Knowing the organisation’s purpose separates the organisation from the rest of the businesses and attains that unique characteristic.
According to Scott and Davis, an organisation is defined as a natural, rational, and open system (Scott & Davis 2008). These aspects focus on particular aspects within an organisation. An organisation is said to be rational when it focuses on achieving a defined set of goals and objectives. The organisation’s management process should be clearly defined, predictable, and rational.
Rational systems in an organisation focus on formalising and goal specification. It focuses on the organisation’s administrative structure, managerial control, and decision-making process. The natural system of an organisation focuses on the informal structure of the organisation. Individuals within an organisation do not follow the formal rules due to pursuing their different interests.
Therefore, the natural system allows them to develop their informal relations that have become influential in managing the behavior of the employees. The open systems perspective determines the relationship between organisations and the external environment. The social environments in which decision-makers will find themselves determine the outcome they will anticipate for the organisation (Willyard 2015). Interserve plc is well suited with the rational systems with specific goals and objectives set out.
Position power is the power an individual attains from authority or position within a company structure or hierarchy. Personal power is the skill and ability depicted in a person to influence other people or events regardless of any formal authority. It is beneficial because it ensures accomplishing things beyond the organisational scope.
Debbie White, the current Chief Executive of Interserve plc, must retain her position even when a New York-based Hedge fund removes the other board members. Debbie can use her positional power to influence organisational change when the other board members are removed. Her position as the Chief Executive gives her the power to influence and make decisions on behalf of the company and demand compliance from the organisation.
Orders completed by our expert writers are
Merger and acquisition entail combining ownership of companies, their operating units, and transactions into one company as a whole. Mergers mainly occur when two entities combine their forces to create one joint company. For acquisition, one entity takes over another entity that is of lower value than they are. Merged companies have a mutual agreement to combine their companies to attain benefits they seek thereby, attaining new names, management, and ownership.
In acquisition, the decision to take over the other entity may not be mutual since an entity of stronger financial status can acquire an organisation with weaker financial status. The smaller entity operates under the name of the stronger entity and most organisation decisions are made from the stronger entity. In addition, merged companies experience dilution of power between the two entities to accommodate each entity while for acquisition, the acquiring entity employs absolute power.
Companies like Interserve Plc that have grown through acquisition may experience some challenges during their operation. The challenges may include integration difficulties where there is difficulty linking financial systems and management systems, with different management styles, of the companies (Amolo 2018).
Inadequate valuation of the target is also a problem where the acquiring company pays too much for the acquired company by failing to evaluate effectively its market share. Moreover, the acquiring company may be required due to market conditions to pay off extraordinary or high-cost debts for the acquired company. The inability of acquiring synergy is the other challenge. The acquiring company may face difficulties in valuing the expected synergies from the acquisition.
The internal environment within a company encompasses all the factors that directly influence the company, such as employees, the corporate culture, and management. The external environment entails all the outside factors that indirectly influence the company’s operation and may include micro and macro-environmental factors.
In Interserve Plc, the internal and external environment can be identified with tools such as SWOT analysis, porter’s five force framework, and PESTLE analysis. A SWOT analysis evaluates the company’s internal environment by determining its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This analysis helps in the decision-making process and evaluating the company’s competitive position in the business environment (Leigh 2009).
PESTLE analysis determines the external factors affecting Interserve Plc by evaluating the political, economic, sociological, technological, legal, and environmental factors. Porter’s five forces also evaluate the external environment by identifying factors affecting competition, existing competitors, suppliers, buyers, substitute products/services, and potential entrants.
Horizontal integration is the process where a company grows by acquiring a similar company in the industry and having the same supply chain. In contrast, vertical integration entails the process of acquiring another company before or after them in the supply chain of command. Through horizontal integration, Interserve Plc can increase its customer base, reduce competition in the market, attain a diversity of products to offer the market, and expand its operation in the market.
Through vertical integration, Interserve Plc may acquire customer boost since they will attain immediate customer access from suppliers and buyers in the chain of command, thereby, increasing their profits. In addition, they will attain reduced transportation costs and acquire higher competitiveness since they can deliver their products directly and quickly to their consumers.
The ethical decision-making process entails decisions that question an individual’s morals and values. Approaches that can be used in determining the decisions to be made in Interserve plc include the utilitarian approach that questions the dilemma of selecting options that will lead to great benefit and least harm (Bartlett 2013).
The option to be selected should lead to an overall best consequence. The virtue approach is the other approach that determines a person’s moral, values, and principle. It determines what kind of person you are by your decisions. The Chief Executive may implement this approach to attain the organisation’s best interest.
The other approach is the common good approach that determines whether the decisions are for the betterment of the individual and community. It depicts the kind of society we want to achieve. Interserve plc may use this approach in deciding on ways to raise funds. In addition to the approaches is the right approach that believes everyone can make their decisions, but if the decision does not respect other people’s moral right, then the act and decision is wrong.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a concept in management where companies manage social, economic, and environmental effects concerning the business operation that aligns with public expectations. CSR in Interserve Plc is important in building the business reputation as a responsible business entity, which can increase its competitive advantage in the business market (Kielmas 2006).
The company with the local community and investment analysts can develop its reputation through transparency. This also increases the customer relations within the business since customers are drawn to companies with good reputations. CSR helps the plc save costs by reducing resource use, emissions, and waste from the company.
It also helps reduce the regulatory burden where good rapport with the local authorities makes the business operate smoothly. CSR also helps the company in improving its profitability and value level. Through waste recycling and the introduction of energy efficiencies, operational costs are reduced and environmental benefits are enhanced.
Implementing CSR in Interserve plc may bring a financial strain since its implementation costs money. The company will incur special costs in implementing CSR because this will be a new method from their daily modes of practice. The interest of the shareholders will also be affected because CSR implementation increases operations costs that need to be paid by shareholders’ funds.
CSR’s main goal is to provide satisfaction and consideration for the needs of the consumers, and this may conflict with the business where its goal is to maximise profits. CSR requires the practice of transparency from the business to the people; this may negatively affect the business’s reputation when they have to be entirely open to the public about their operation, goods, and services.
A joint venture partnership entails two or more businesses combining their expertise and resources to attain a specific goal or benefit. The businesses share the rewards and risks attained from the business. Interserve Plc can join a joint venture to attain entry into new markets, helps in the business expansion, attain more resources, develop new products, and gain technical expertise.
There are different types of the joint venture such as limited co-operation where the businesses agree to collaborate in specific and limited ways and separate joint venture account where the two businesses set out a new company to handle a certain contract for a particular period. A business partnership is also part of a joint venture where the two companies can merge their operations in business.
Deciding which joint venture to join requires Interserve plc to evaluate effectively the risks attained, rewards, management style to be followed, and how the business operations will be handled. Interserve Plc can major into the business partnership to attain more benefit now and in the future, as the business picks up and grows, this will provide it with an opportunity to market entry, accessing of greater resources, distribution networks, and sharing of risk with the partner. For a joint venture partnership to be successful, the businesses should identify the right ventures, plan their relationship, assess their readiness to venture into a partnership, and mutually agree on how the business will be operated.
Anyone working under a contract is a contractor. Still, where the work to be performed is part of fulfilling a buyer in another contract, where he or she acts as supplier, then the seller is referred to a sub-contractor. All suppliers are contractors since buying and selling transactions have contracts. Selecting suppliers and sub-contractors requires a strategic approach based on the business strategy and priorities.
Choice in the strategic selection depends on their reliability, service, your value for money, and the quality needed. Selection criteria that can be used include strategic thinking before selecting a supplier: the supplier selected should offer products and services that match that of the business needs and achievement desires.
The supplier’s values such as reliability, quality delivery, financial security, open communication, and a partnership approach are some things to be looked into during selection (Mahdi et al. 2012). Supplier and sub-contractors can also be selected by identifying their potential through recommendations, business advisors, directories, trade associations, and exhibitions. Furthermore, to attain the best supplier and sub-contractor, Interserve plc should identify their needs, goals, and objectives to enable them to find a supplier who matches their needs and avoid being tempted by sales patches that do match their requirement.
Amolo, N.T., 2018. Challenges of Mergers and Acquisition Strategy between Uap Holdings and
Old Mutual Plc (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi).
Bartlett, D., 2013. Management and business ethics: a critique and integration of ethical
decision‐making models. British Journal of Management, 14(3), pp.223-235.
Kielmas, M., 2006. Pros & cons of corporate social responsibility. Retrieved from Chron:
http://smallbusiness. chron. com/pros-cons-corporate-social responsibility-56247. html.
Leigh, D., 2009. SWOT analysis. Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace:
Volumes 1‐3, pp.115-140.
Mahdi, I.M., Riley, M.J., Fereig, S.M. and Alex, A.P., 2012. A multi‐criteria approach to
contractor selection. Engineering, construction, and architectural management.
Scott, W.R. and Davis, G.F., 2008. Rational, Natural, and Open System Perspectives.
Willyard, K., 2015. Rational, Natural and Open System Perspectives of Organisations.
To write a master’s assignment: