Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness.
The importance of the English language has increased due to its use for business communication (Bogdandy, et al., 2020). The quality of education in rural China is strikingly inferior to urban education due to differences in income levels of the rural residents compared to the urban residents along with the additional subsidies received by urban residents for education, medicine and housing. As per Fu (2005), children in rural schools of China have poor English speaking capabilities compared to their urban counterparts due to lower expenses on education and the lack of qualified English teachers.
Educational development in rural China has been marginalized due to very little sponsorship from the families and local townships. In contrast, the government continues to sponsor education in the urban areas, leading to the widening gap in the English-speaking abilities of the rural Chinese students.
Artificial intelligence is used in education and teaching delivery for adaptive learning and automated teaching experience along with eradicating inequalities in opportunities (Rayradar, 2019). AI has the potential to eradicate educational inequalities while promoting learners from rural and disadvantaged areas in China to receive the highest levels of pedagogy.
Emotech is a UK based organisation specialising in the domain of artificial intelligence and the organisation has utilised the technology infrastructure in the field of multimodality for English education delivery (Rayradar, 2019). Using a teaching assistant tool benefits the development of the pupils while learning a second language while making the natural human interaction mode for the evaluation of solutions (Graesser, et al., 2018).
While the realities of how AI is used in the classroom and how it integrates with pedagogy have not been researched in depth. The research intends to conduct a participatory action investigation for arriving at the outcomes of integrating the teaching assistant tool for using multimodal capabilities while teaching the English language in rural Chinese schools. This involves different stakeholders (teachers, students, AI product managers and headteachers) to integrate and improve the usage of a multimodal English teaching assistant tool in classrooms.
The research will investigate the integration of a multimodal English teaching assistant tool into rural China classrooms by conducting participatory action research.
The research objectives will be:
The research question is:
How can using an AI-supported tool provide a sustainable and effective means of enhancing the English learning of young learners in rural China?
Sub-question: Understanding what is happening and the existing problem:
According to Hu, (2005), English is a globally accepted language spoken by millions of people and remains essential for securing prospective employment opportunities across every nation. However, there is less scope of interacting in English for the students in the rural regions of China due to the lack of central government funding for primary education and the lack of qualified English teachers.
This results in ineffective language learning for the rural students and uncertainty over future employability. In China, the decision of the policymakers and ministry of education has resulted in a transformation in English language education with a shift from grammar-based to communicative-based pedagogy. This has been due to the realisation of the importance of learning and speaking English for communication. This decision comes from increasing communicative competence as a goal of 21st-century second/foreign language in China.
As per Hummel (2020), the theories of English language teaching include Behaviorist, Innatist, Cognitivist, and Interactionist. The Behaviorist theory advocates the process of drill and practices through rote memorisation of the language. Innatist theory advocates the learning process to be hardwired in an individual as learning a second language like English is considered similar to the native language. The cognitive theory advocates the process of learning to be through practice and noticing while using a language format. Lastly, the interactionist theory states the process of English language learning to be through the process of speaking with proficient speakers of the English language.
As per Rodrigo, et al. (2019), AI-powered Intelligent tutoring systems or ITS provides customised instruction and learning experience to the learners along with integrating real-time feedback without the requirement of human intervention by a teacher. As per Benton, et al. (2021), ITS enables language learning effectively and meaningfully with multiple computing technologies.
It is used across classrooms to enhance the learning experience by integrating technology as a teaching assistant tool (Luckin, 2017). The latest ITS are developed with the basic AI algorithms to deliver a multimodal teaching experience (Gillani and Eynon, 2014). As per Crow, et al., (2018), Artificial Intelligence based teaching assistants includes audio and video capture for understanding the standard English pronunciation of the students and giving them feedback for strengthening their oral communication and writing abilities along with the accent.
According to Spikol, et al., (2018), multimodal learning is a concept of teaching using multiple methods including visual, auditory, kinaesthetic, reading and writing. The multimodal learning experience can be enhanced with intelligent tutoring systems powered by AI and machine learning, leading to learning any language or subject with practice (Chango, et al., 2021).
The multi-model technology of the teaching assistant tools can facilitate the delivery of English language training in Chinese classrooms by integrating multiple categories of data and analysing text, voice and space. Multimodal English teaching with the help of a digital assistant tool can benefit the requirements of pure speech technology for a quiet environment and improve pronunciation accuracy through speech recognition.
Orders completed by our expert writers are
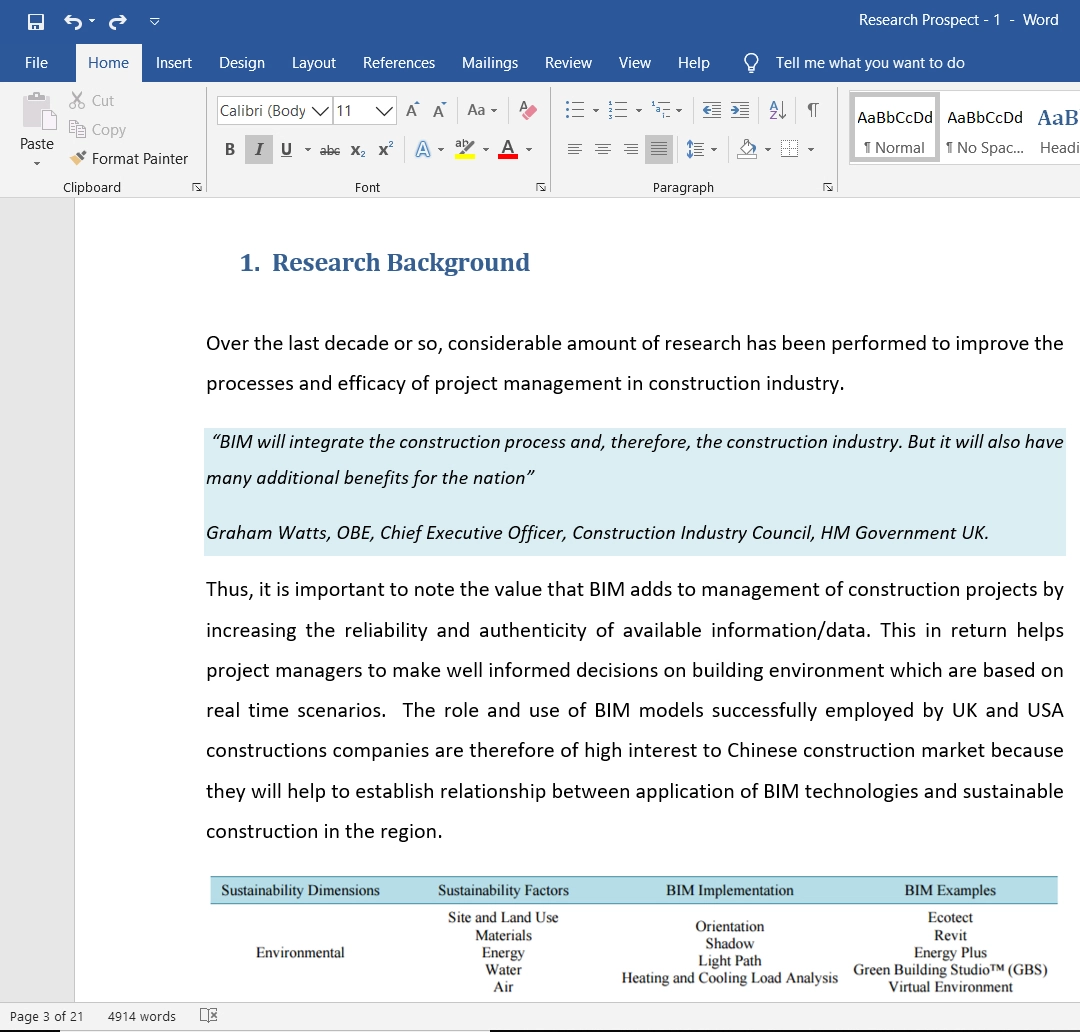
The research will analyse the possibility of integrating a multimodal English teaching assistant tool in the Chinese rural classrooms with the help of a participatory action study. The following tool used in a Chinese research school will be used in this investigation.
The research will include diagnosis of the English learning issues at rural Chinese schools for designing the multimodal teaching assistant by collaborating with product designers, teachers, students, language experts and researchers to discuss current problems of using this tool in a real classroom. This will be done using students’ data from the tool, interviews, surveys and second language learning theories.
The research will be conducted with the interpretivism philosophy to interpret the individual elements in the research topic by integrating human interest (Saunders, 2011). This will include an inductive approach for establishing theory regarding the applicability of multimodal English teaching assistant tools in the Chinese rural classrooms paired with an exploratory design to excavate more knowledge on the subject.
The interpretivism research will include in-depth investigation and apply qualitative methods for data collection and analysis (Clarke, et al., 2013). This will also include a focus on narratives and perceptions and generate new standings and wall views regarding the use of multimodal English language teaching assistant tools.
The data for the research will be collected by conducting semi-structured interviews with 6 developers of Emotech and 6 teachers selected from Chinese rural schools. The interview will be conducted via video conferencing using Zoom software air and open-ended questions will be asked to the participants. The thematic analysis technique will be used for data analysis during which similar patterns will be identified from the responses of the interview respondents for developing themes. These things will be used for an extended literature review by consulting secondary information sources.
Benton, L. et al., 2021. Designing for “challenge” in a large‐scale adaptive literacy game for primary school children. British Journal of Educational Technology, 52(5), pp. 1862-1880.
Bogdandy, B., Tamas, J. & Toth, Z., 2020. Digital transformation in education during covid-19: A case study. In 2020 11th IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications (CogInfoCom). s.l., IEEE, pp. 000173-000178.
Chango, W. et al., 2021. Improving prediction of students’ performance in intelligent tutoring systems using attribute selection and ensembles of different multimodal data sources. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 33(3), pp. 614-634.
Clarke, J., Tamaschke, R. & Liesch, P., 2013. International experience in international business research: A conceptualization and exploration of key themes. International Journal of Management Reviews, 15(3), pp. 265-279.
Crow, T., Luxton-Reilly, A. & Wuensche, B., 2018. Intelligent tutoring systems for programming education: a systematic review. s.l., In Proceedings of the 20th Australasian Computing Education Conference, pp. 53-62.
Fu, T.M., 2005. Unequal primary education opportunities in rural and urban China. China Perspectives, 2005(60).
Gillani, N. and Eynon, R., 2014. Communication patterns in massively open online courses. The Internet and Higher Education, 23, pp.18-26.
Graesser, A., Hu, X. & Sottilare, R., n.d. Intelligent tutoring systems. In International handbook of the learning sciences, pp. 246-255.
Hu, G., 2005. English language education in China: Policies, progress, and problems. Language policy, 4(1), pp. 5-24.
Hummel, K.M., 2020. Introducing second language acquisition: Perspectives and practices. John Wiley & Sons.
Luckin, R., 2017. Towards artificial intelligence-based assessment systems. Nature Human Behaviour, 1(3), pp.1-3.
Rayradar, 2019. Emotech, a well-known British AI company, joins Huawei in launching a multimodal English teaching assistant program. [Online] Available at: https://www.rayradar.com/2019/09/20/emotech-a-well-known-british-ai-company-joins-huawei-in-launching-a-multi-modal-english-teaching-assistant-program/ [Accessed 22 Dec 2021].
Rodrigo, M. et al., 2019. Ibigkas!: The Iterative Development of a Mobile Collaborative Game for Building Phonemic Awareness and Vocabular. Computer-Based Learning in Context, 1(1), pp. 28-42.
Saunders, M., 2011. Research methods for business students. United Kingdom: Pearson Education.
Spikol, D., Ruffaldi, E., Dabisias, G. & Cukurova, M., 2018. Supervised machine learning in multimodal learning analytics for estimating success in project‐based learning. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 34(4), pp. 366-377.
To create a Ph.D. dissertation outline, follow these steps: