Sample Master Business Literature Review
Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness. Read a guide about how to write a literature review.
Extended Critical Argument with SLR in Business Research for Entrepreneur Personal Branding for SME Startup Success
This extended critical argument will be highlighting the three main areas on which SLR is established. We will be evaluating an entrepreneur’s branding in an SME in this regard.
Executive Summary
Emerging social networking and the internet quest also brought in two distinct phenomena: Social networking is a modern communications tool for SMEs and consumers to connect in a corporate sense. This thesis tries to investigate the effect of social networking on small businesses. This approach uses a systematic literature review (SLR). The method is carried out by reading journals that deal with research matters SME users in all nations exhibited common effects of social network use SMEs’ uses of social media can be linked to their goals. Its influence is mostly because of clients, partners, partners, and rivals. The results are, however, broad and impersonal. Therefore, more study is needed to understand better the factors that influence social media use in small businesses.
Introduction
Small and medium businesses are essential for many countries. Because of their contributions to creating employment and economic growth that positively affect the world, small businesses pose fresh obstacles in today’s economy because of increased variation and competitiveness brought about by globalization. Small- to medium-sized enterprises provide both financial and human capital that are very limited on the other. Conversely, to help SMEs conquer networks outside their current markets, proximity to external funding, and product creativity (Khedher, M., 2014).
The findings are in part backed by information and communication technologies, which have impacted sales for the last two decades. The industry is riding the internet’s coattails. The expansion of the internet has given rise to two significant effects: social networking and search engines. Social networking is a modern engagement tool that businesses may use to engage with consumers.
Social networking is a credible and up-to-to-date resource. Social networking enables quick communication and helps businesses have an accurate sense of consumer desires and better serve them. The rise of social networking has given small businesses new reasons to become more ambitious in marketing, labels, or services. The number of social media users grows per year.
Additionally, both kinds of social networking sites continue to grow in use. Social networking is a routine tool for everyday use. It has triggered conduct improvement for the company to handle. Strategies and tools have completely shifted with the emergence of social networking. Today, different social media channels have become an essential part of all marketing efforts, particularly for SMEs.
.In contrast, social networking seems to have different advantages. It is essential for the consumer base and retaining your current customers. Often, using social networking for consumers will help to fuel new product development. According to an industry study, most advertisers agree that social networking is a part of their overall communication strategy. Using social networking is significantly less expensive and more efficient than most contact methods.
More companies are using social networking to boost their brand recognition, consumer care offerings and increase revenue. Many businesses have social networking use as an essential goal also, marketing through social media may improve a company’s image. Customers have links to different consumer experiences and feedback using social media.
Based on the information above, it seems that SMEs have accepted the presence of social media. Social networking has functionalities. This research unveiled seven blocks of social network features, including personality, conversation, appearance, and credibility.
Concerning small businesses, each social media has its unique influence. Studies can be done on how social networking is utilized for small businesses. No analysis so far has been able to test the validity of this hypothesis. (Nyoni, T. ,Bonga and W.G., 2018)
Modus
Social media’s impact on small businesses has been widely studied before. Some earlier research explored the social networking use of small businesses and how they use it to drive their engagement in the industry. So far, there has not been any comprehensive research into how social networking influences the sales phase in SMEs. (Wardati, N.K., Mahendrawathi, and E.R., 2019). Will the use of social media have an impact on small business sales? (not Citation Analysis or Completion) (SLR). In the first step of SLR, previous pieces of literature will be collected as data.
Each stage was executed in order:
- Keyword searching for relevant texts under the requirements specified in the plan.
- Except for literature that does not follow the inclusion/exclusion criterion.
- Reading articles whose titles follow the criteria and elimination occurred until involuntariness.
- Determining the full authorship of the literature and determining the content
- They use keywords such as “social networking” while searching the Science Direct index “S.M. “small-enterprises” and “sales” or “sales.”
- In Emerald, keyword, and content search method was used in the journals:
either “social media “OR “S.M.” and “small businesses “SME’s” AND “selling.”
Number of journals generated at each quest stage and journal findings shown in Table 1 center
| No. | Criteria | Science Direct | Emerald Insight (Abstract) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Corresponding with the entered keyword | 1201 | 1359 |
| 2 | Journal / Article received | 213 | 545 |
| 3 | Published in 2017-2018 | 73 | 241 |
| 4 | Keywords correspond with the title, abstract, and keyword | 17 | 19 |
| 5 | The abstract is appropriate to answer the problem formulation in the study | 11 | 13 |
The next step in the literature review is to weed out irrelevant, and important literature Inclusion requirements are literature review criteria, although exclusion criteria are already existing literature review criteria. The below are the inclusion criteria:
- The article included in this issue
- The journal studies the social media use
- The findings were first presented in 2018
- The paper journal is available in English (Q1 and Q2)
- The research requirements are as follows:
- This literature has little to do with small businesses and does not meet their business study needs.
- Only scholars can find the literature (not in English)
- It was out before 2017
After the literature has been identified, the next phase is to evaluate the quality. Evaluation of the literature is dependent on the OR operation. We’ve looked up titles, keywords, and abstracts for 18 publications. Out of the 18 papers, they’ll be choosing according to the principles. the papers are the last of the screening process to gain a greater understanding, will be studied to see how the papers represent the study’s issue or concept. (Costa, 2019)
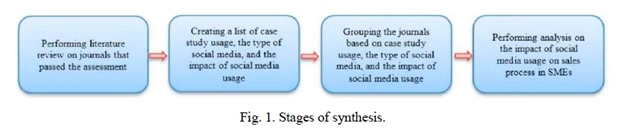
Synthesis is the final move. This process was carried out to resolve the issue outlined in the introduction. The Systematic Literature Review (SLRLC) was done in several steps, as seen in Fig. 1.
The literature analysis was completed, 12 of the 18 journals were selected. The analysis covers 12 articles. The findings of the literature analysis of 12 approved articles were arranged and organized based on the forms of social media, their use, and the case studies applied. A short overview of the 12 selected articles is designed to explain further the literature relevant to the formulation of the issue. The last move was to study social networking on small businesses from the systematic literature review. The response to the question can be found.
Outcome
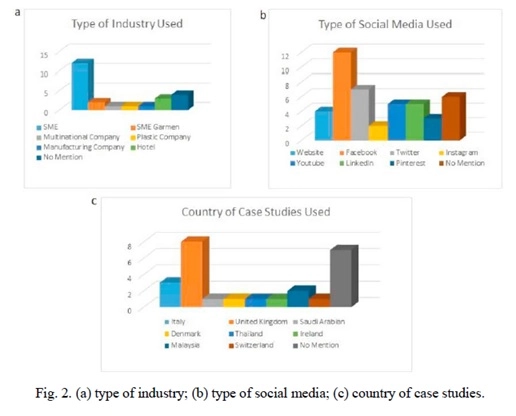
According to the synthesis findings, there are 12 papers included in this analysis. We collected case studies from many countries. Furthermore, the forms of social networking and usage of each industry are different. can be seen in Fig. 2
Many journals used in the field refer to small and medium-sized businesses only, as in Fig. 2a Fig. 2b reveals that traditional social networking has been heavily researched. People commonly use Facebook, and that’s why it is convenient to learn.
Such case studies also included social networking, for example, Facebook and Twitter. Much of the published studies have been completed in the U.K. Most U.K. small businesses use I.T. (Matthews, R.S., Chalmers, D.M. and Fraser, S.S., 2018)
Social networking has various corporate purposes, such as communications, public relations, customer care, human services, employee training, and client relations. Web 2.0 philosophy and technologies form the basis of social networking, which aids the production and distribution of information developed by users.
Many social media websites involve social networking sites (SNS), forums, newsletters, microblogging, product/service ratings, and video sharing. Social networking promotes sharing and material creation through individuals. Internet networks such as Facebook, YouTube, Instagram, TripAdvisor, forums, Wikipedia, and review websites are used for sharing interactions and interactions. As long as consumers have access to mobile devices such as smartphones or laptops, they will remain connected with social media. (Yadav, N., Gupta, K., Rani, L., and Rawat, D., 2018.)
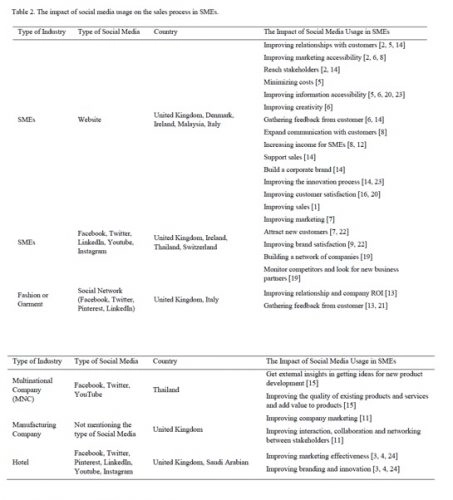
Following the literature community, a more thorough review of social network use of the sales mechanism was conducted on 12 trade papers used as testing resources. The effect of social network use on small businesses is visible in Table 2.
Based on the literature review, social networking had several effects on the sales phase. 12 studies say social networking had little impact on small business sales operations.
Any of these journals teach you about consumer engagement, as well as measuring customer traits on social media. Consequently, social media use (SMEs) impacts were observed to apply to diverse sectors and different forms of social communication.
It can be widely inferred that the use of social networks is widespread among small businesses. Anything hinges on the form of small businesses and social networking. They use social media for business goals. Nearly all of the results apply to small and medium-sized companies’ sales and marketing processes, including their interaction with clients, corporate associates, and rivals. (Secundo, G., Del Vecchio, P. and Mele, G., 2020)
Social networking is classified into social bookmarking, social networks, downloading, knowledge, and reporting on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, and Pinterest, becoming part of social publishing. A majority of companies use social messaging through social networks specific to the business’s plans and goals that utilize social networking. Additionally, therefore, much of the focus demographics with the usage of social media utilise social media.
The influence of social media on the small-entry phase will boost earnings (examples of television programs, films, books). However, this is not the norm in primary industries such as agriculture, which includes low-value-chain knowledge but just low information intensity. Many stakeholders, such as customers and staff, are willing to engage in the active use of social media. Businesses would assume a more critical, online, interactive, and transformational position with all their SMEs.
With this, companies will encourage and lead to the birth of entrepreneurial [generations]. Based on recent experience, SMEs get input from customers from social media. In other words, SMEs explore social media with their corporate interests. Marketing analysis solicits information from different stakeholders (customers, vendors, and employees) to make businesses aware of consumer demands and use those findings to produce new goods or services.
Additionally, social network use helps reduce expenses, creates stronger consumer connections, and allows access to relevant knowledge. extensive promotion doesn’t take a big expense on small and midsize businesses. (Pittaway, L. and Cope, J., 2007)
The only way for a small business to expand its reach is to penetrate new markets, even though they have only a handful of human capital and insufficient financing. Social media is for businesses is to better advertise, collaborate, and network with stakeholders. This kind of organization wants more than a singular platform.
Social networking facilitates scheduled and constructive selling. Social networking is created by fresh and emerging tools that affect the market. As mentioned by The Industrial Marketing and Purchasing (IMP) theory will back this up by citing the relevance of social networking in tandem with other interconnected tools. First, social media is used by salespeople and sales managers.
Thirdly, social networking is successful in selling activities. Understanding the social networking tools and the real and future contribution of social network capital could be different. The popularity of social networking in small businesses relies on the company’s status. (Morais, F. and Ferreira, J.J., 2020)
SMEs don’t care for social networking. These issues are exacerbated by elderly business owners who find social networking challenges, which causes them to avoid social networking and utilize other tools. This research highlights the primary targets of social networking adoption in small to medium-sized businesses. Social media’s popularity often relies on how small businesses manage business functionality. Nevertheless, certain issues need further examination:
- Effective application of social networking strategies benefits small to medium-sized companies. Small to medium-sized businesses (SMEs) can easily use social media. Social networking is more about intent, with no rules. The use of social media has been studied among small and medium-sized businesses. Social media’s position and effect are highly dependent on other services inside small and medium-sized companies. Therefore, there is a need to study the social networking effect on small businesses.
- Alignment between social network functionalities to increase SMEs’ efficiency is different from any social networking service. Social networking was placed in the same study to be functional. This partnership tested how social networking built on top of SMEs’ usage would support social strategies.
- Social media’s impact on small businesses and executing a successful social networking campaign, results, and perceived effects must also be factored. Allow it to demonstrate how much social media contributes to their development.
Hire an Expert Literature Review Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in the academic style
- 100% Plagiarism-free & 100% Confidential
- Never resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Conclusion
It is to find out how social networking affects small business sales methods by a systematic literature review (SLR). From the findings of several journals, we will determine certain social network impacts. The formula was applied to both of these impacts. One consequence of small business social networking use is greater exposure to customers and better communication, and another is greater content exposure at a lower rate. The impacts are variable, depending on the market and the social network.
This study looks at the effects of social network use on various sectors of small businesses. For the most part, this is a narrative of SMEs’ overall success. More analysis is needed to understand better the reasons behind social media usage in a wide range of small businesses. We will need to explore the connection between small businesses and social networking strategies.
SLR Protocol
Change of Record
Document History
| Version 1.0 | The first draft of Protocol |
| Version 1.1 | Correction of spelling mistakes |
| Version 1.2 | Minor revision made after expert review of Version 1.1 Protocol |
| Version 1.3 | Revisions made to Quality Assessment Forms |
| Version 1.4 | Final Version of Protocol |
Background
Although small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) account for 99 percent of private-sector firms, policymakers often ignore them, and the importance of the SME leader’s role is vastly underestimated.
Given this, is information management (K.M.) in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) getting adequate coverage in K.M. research?
A recent study1 summarized and critiqued the literature on information management (K.M.) in SMEs, offering a summary of the state of the field and proposing a potential research agenda. The research used a systematic literature review approach to analyze 89 articles written in ten publications devoted to knowledge management. Personal branding can add up to the value of the SME as it directly affects the business the SME is doing. (Reed and C.J., 2018)
Research Questions
The aims of the SLR are to
- To figure out the importance of self-branding in the SME ecosystem.
- Collect and examine the information from these studies to determine the potential advantages and drawbacks of using personal branding to add value to the SME.
- A realistic view of research in the field.
- To provide a proper frame of reference.
- To find the ultimate answer to the question: “Have entrepreneurs been good at marketing themselves.”
Strategy for Search
This segment explains the strategy for primary study searching. The quest strategy aims at identifying and collecting all literature that meets the inclusion and exclusion requirements set out. A hybrid quest approach will be developed, which involves both automated database scans automatically and manual meeting searches and journal searches. The quest technique was developed based on the experience of conducting a comprehensive mapping analysis. Note, publishing year is not limited as trial searches mean that a manageable number of findings can be provided by the devised quest technique that does not require further reduction.
Criteria for Selection
This segment outlines the conditions for inclusion and exclusion to ensure that only valid literature is admitted into the SLR.
Criteria for Inclusion
- Publications can only study the usage of entrepreneurial marketing abilities that have already branded themselves to add value through their SMEs.
- Documents including an observational analysis or a ‘learned lesson’ feature (experience report) shall be included.
- The latest article used in many journals reporting the same research.
- Release date is not a deterrent to inclusion.
- Where applicable, grey literature (such as technical articles and government reports) would be approved.
Criteria for Exclusion
- Publications shall be omitted if their primary emphasis is not on the marketing expertise of entrepreneurs.
- Documents and analyses shall be omitted when the summary is accessible but not the complete text.
- Publications that are not published in English shall be omitted.
- All is omitted by letters, editorials, and opinion papers.
Selection Process
The selection method will be conducted by one researcher (the author) after an interval (of one month) to validate the selection process. In addition, a second researcher (a Ph.D. supervisor) may independently pick and equate a random subset of the archived search results with the search results they have conducted. By following these methods, the inclusion and exclusion conditions may be checked and validated.
The selection process is split into two phases:
- Publications discovered during the initial review are analyzed based on their title and abstract study—meaningless literature.
- Publications chosen during Phase 1 and open to further review (i.e., complete text reading). It was done to ensure that this publication includes details important to the research and evidence that can be retrieved for later review.
Study Quality Assessment
Each publication would be evaluated for its content. The quality testing process will proceed simultaneously with retrieving appropriate data and ensuring that a specific study result makes a meaningful contribution to the SLR.
Extraction of Data
This portion explains how the necessary knowledge is gathered from each publication.
Collection of Data
All details are retrieved by a single reviser (the author). A second evaluator (a Ph.D. supervisor) may derive knowledge separately from a random collection of publications. The findings can then be compared and compared. There are substantial irregularities in testing this random sample, consultations with the assessors, and a second doctoral supervisor to address the issue.
Synthesis of Data
The data synthesis technique will not be finalized until the effects of the SLR are aggregated. However, it is anticipated that details will be tabled in various tables relating to study questions.
If you need assistance with writing your literature review, our professional literature review writers are here to help!
Study Limitations
The investigator does not influence one part of the analysis concerning the electronic databases used during the SLR. Although these automated tools immediately retrieve the data. It could lead to two searches being genuinely similar and subsequent experiments to reproduce the study accurately.
Protocol Validation
The protocol submitted was validated after two expert reviewers were granted a previous edition (1.1). The modifications proposed by these reviewers were included in the provided procedure.
References
Nyoni, T. and Bonga, W.G., 2018. Anatomy of the small & medium enterprises (SMEs) critical success factors (CSFs) in Zimbabwe: Introducing the 3E model. Dynamic Research Journals’ Journal of Business & Management (DRJ-JBM), 1(2), pp.01-18.
Wardati, N.K. and Mahendrawathi, E.R., 2019. The impact of social media usage on the sales process in small and medium enterprises (SMEs): A systematic literature review. Procedia Computer Science, 161, pp.976-983.
Costa, E., Soares, A.L. and De Sousa, J.P., 2016. Information, knowledge and collaboration management in the internationalization of SMEs: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Information Management, 36(4), pp.557-569.
Matthews, R.S., Chalmers, D.M. and Fraser, S.S., 2018. The intersection of entrepreneurship and selling: An interdisciplinary review, framework, and future research agenda. Journal of Business Venturing, 33(6), pp.691-719.
Yadav, N., Gupta, K., Rani, L., and Rawat, D., 2018. Drivers of sustainability practices and SMEs: A systematic literature review. European Journal of Sustainable Development, 7(4), pp.531-531
Secundo, G., Del Vecchio, P. and Mele, G., 2020. Social media for entrepreneurship: myth or reality? A structured literature review and a future research agenda. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research.
Morais, F. and Ferreira, J.J., 2020. SME internationalization process: Key issues and contributions, existing gaps, and the future research agenda. European Management Journal, 38(1), pp.62-77.
Pittaway, L. and Cope, J., 2007. Entrepreneurship education: A systematic review of the evidence. International small business journal, 25(5), pp.479-510.
Nolan, C.T. and Garavan, T.N., 2016. Human resource development in SMEs: a systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Management Reviews, 18(1), pp.85-107.
Reed, C.J., 2018. Personal branding mastery for entrepreneurs. Evolve Global Publishing.
Iso-Berg, M., 2015. Entrepreneur’s Identity in Personal Branding-A Study on Building the Brand.
Brems, C., Temmerman, M., Graham, T. and Broersma, M., 2017. Personal branding on Twitter: How employed and freelance journalists stage themselves on social media. Digital journalism, 5(4), pp.443-459.
Raftari, M. and Amiri, B., 2014. An entrepreneurial business model for personal branding: proposing a framework. Journal of Entrepreneurship, Business, and Economics, 2(2), pp.121-139.
Khedher, M., 2014. Personal branding phenomenon. International journal of information, business, and management, 6(2), p.29.
Frequently Asked Questions
To write a master’s level literature review:
- Define the scope and purpose.
- Search and select relevant sources.
- Summarize and analyze each source.
- Identify trends and gaps.
- Organise into themes.
- Critically evaluate sources.
- Synthesize findings coherently.